What is real number
What is real number
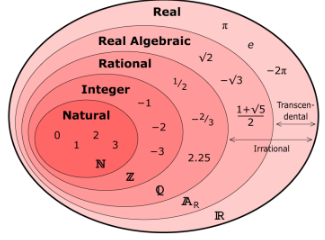
Real numbers are nothing but numbers that include both rational and irrational numbers, in other word the combination of rational and irrational numbers . Rational numbers such as integers (-2, 0, 1), fractions(1/2, 2.5) and irrational numbers such as √3, π(22/7), etc., are all real numbers.In mathematics, real numbers are a set of numbers that include both rational and irrational numbers. Real numbers can be represented on a number line and are used to describe quantities that can be measured or expressed as decimal numbers.
Real numbers include whole numbers (such as 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.), integers (such as -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, etc.), rational numbers (such as fractions or decimals that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers, like 1/2 or 0.75), and irrational numbers (such as π or the square root of 2, which cannot be expressed as a fraction and have non-terminating or non-repeating decimal expansions).
The set of real numbers is denoted by the symbol ℝ. Real numbers have various properties, including the ability to perform arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. They also have an ordering property, which means they can be arranged in a meaningful order from smallest to largest or vice versa.
Real numbers are fundamental in many branches of mathematics, including algebra, calculus, and analysis. They are also widely used in various scientific fields to describe and measure quantities in the physical world.
Type of real number
Real numbers can be categorized into different types based on their properties. Here are some common types of real numbers:
Rational Numbers: Rational numbers are real numbers that can be expressed as a ratio of two integers (a fraction). They can be written in the form p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not zero. For example, 3/4, -2/5, and 0 are all rational numbers.
Irrational Numbers: Irrational numbers are real numbers that cannot be expressed as a fraction or a ratio of two integers. They have decimal representations that neither terminate nor repeat. Examples of irrational numbers include √2 (the square root of 2), π (pi), and e (Euler's number).Integers: Integers are whole numbers (positive, negative, or zero) without any fractional or decimal parts. They include positive numbers, negative numbers, and zero, such as -3, 0, 1, and 5.Natural Numbers: Natural numbers, also known as counting numbers, are positive integers excluding zero. They are used for counting and ordering objects. Natural numbers start from 1 and go infinitely, such as 1, 2, 3, 4, and so on.Whole Numbers: Whole numbers are similar to natural numbers but include zero as well. They consist of all non-negative integers, including zero. Whole numbers are 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on.Prime Numbers: Prime numbers are positive integers greater than 1 that have no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. They cannot be formed by multiplying two smaller positive integers. Examples of prime numbers include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on.
These are some of the main types of real numbers, each with its own distinct properties and characteristics.



Comments
Post a Comment